


Next: Single Dish Radio Telescopes
Up: Interferometry and Aperture Synthesis
Previous: Aperture Synthesis
Contents
The Fourier Transform
Table 2.1:
Fourier transform pairs
| Function |
Transform |
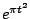 |
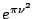 |
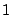 |
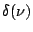 |
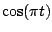 |
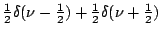 |
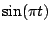 |
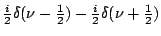 |
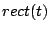 |
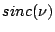 |
The Fourier transform 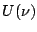 of a function
of a function 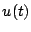 is defined as
is defined as
and can be shown to exist for any function 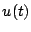 for which
for which
The Fourier transform is invertible, i.e. given 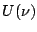 ,
, 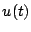 can be obtained
using the inverse Fourier transform, viz.
can be obtained
using the inverse Fourier transform, viz.
Some important properties of the Fourier transform are listed below (where
by convention capitalized functions refer to the Fourier transform)
- Linearity
where 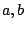 are arbitrary complex constants.
are arbitrary complex constants.
- Similarity
where 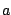 is an arbitrary real constant.
is an arbitrary real constant.
- Shift
where 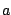 is an arbitrary real constant.
is an arbitrary real constant.
- Parseval's Theorem
- Convolution Theorem
- Autocorrelation Theorem
Some commonly used Fourier transform pairs are:



Next: Single Dish Radio Telescopes
Up: Interferometry and Aperture Synthesis
Previous: Aperture Synthesis
Contents
NCRA-TIFR
![]() of a function
of a function ![]() is defined as
is defined as